Trending Assets
Top investors this month
Trending Assets
Top investors this month
How to Read a 13D and 13G Filing
Example: 13D Form from Elon Musk
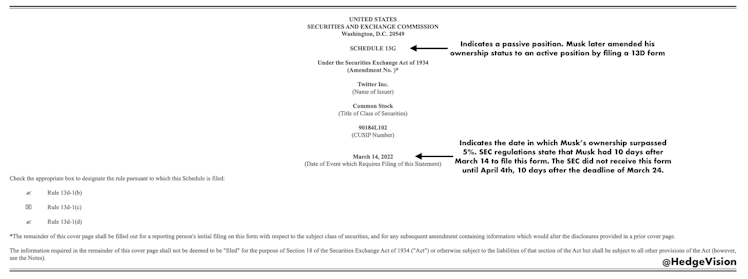
Elon Musk 13G Form for Twitter: Cover Page
Musk made two mistakes when filing his initial 13G form. First, he was 10 days late. SEC regulations state that an institutional investor must file a 13D/G form within 10 days of exceeding 5% ownership. Musk is classified as a regular institutional investor. Therefore, the deadline to file the 13G form was March 24; Musk filed the form on April 4th.
Musk allegedly made $156 million due to his late disclosure.
If Musk had made his disclosure on time, chances are he would have to buy further shares at higher prices due to his effect on the stock price.

Elon Musk 13G Form for Twitter: Main Page
Second, the amount of shares directly owned by Musk was overstated. He filed an amended 13D form the next day on April 5th to correct this. With the 13D filing, the Tesla CEO also converted his position status from passive to active.
Initial 13G Filing on April 4th: 73.48 million shares.
Amended 13D Filing on April 5th: 73.11 million shares.
Example: 13G Form from Vanguard (QII)
Once a qualified institutional investor (QII) crosses the 10% threshold, they must file a 13D/G form to the SEC. However, the deadline to submit the form differs under certain circumstances as well. Additionally, the position size change thresholds to trigger a 13D and 13G amendment differ. Besides that, the two forms are, for the most part, similar. Let’s get into the details.
Pictured below is the cover page of an amended 13G form depicting Vanguard’s acquisition of Twitter during March of 2022. Vanguard is a passive investor and holds Twitter across its ETFs. Vanguard is classified as a qualified institutional investor (QII), so the circumstances for it to file a 13D or 13G form are different from regular institutional investors. QII’s include pension funds, banks, investment advisors, insurance companies, etc.

Vanguard 13F Filing for Twitter: Cover Page
The “Date of Event Which Requires Filing of this Statement” of March 31st, 2022 may be the most misleading statement on the cover page. This date does not indicate the actual date of transaction. Rather, it discloses the date that triggered the filing.
The exact date(s) that Vanguard purchased TWTR stock to cause it to own a 10% stake is unknown. However, it was some time during March. The SEC received Vanguard’s amended 13G form on April 8th and subsequently disclosed it to the public.
Take a look at Vanguard’s transactions for the past 3 months. All the filings fall within the first 10 days of the month.
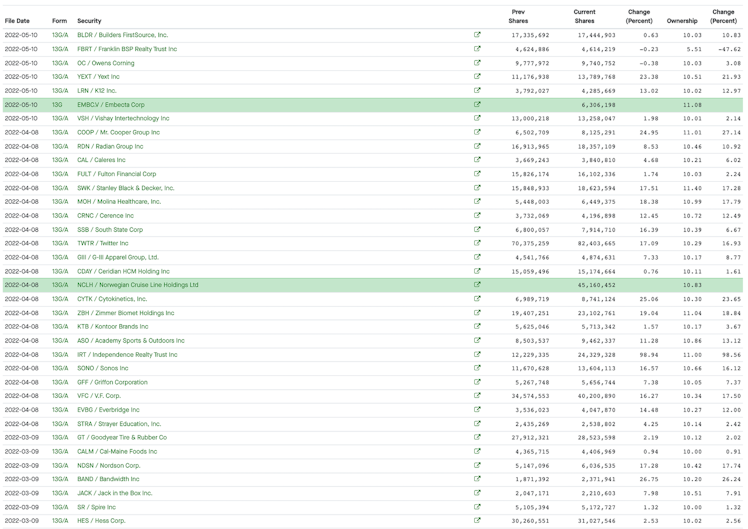
Vanguard 13G Filings
Let’s go to the next page, which provides all of the details of the transaction:

Vanguard 13F Filing for Twitter: Main Page
Vanguard’s holdings of TWTR stock are over 10%, which triggered this filing. See #11.
This page is pretty clean-cut and details Vanguard’s voting power, number of shares owned, and any joint ownership. #9 and #11 are what I usually look for.
Since this is a passive 13G filing, it means that Vanguard does not seek to influence Twitter’s business decisions. For its ETF holdings, Vanguard has voting power and generally sides with the company’s management during voting events.
Read the complete piece here: https://foryoureyesonly.substack.com/p/how-to-read-a-13d-and-13g-filing?s=w
foryoureyesonly.substack.com
How to Read a 13D and 13G Filing
Inside Elon Musk's blundered 13G filing for Twitter
Already have an account?