Trending Assets
Top investors this month
Trending Assets
Top investors this month
Android and Google Play Store
Operating systems are the mind of electronic devices such as computers, mobiles, tablets, smartwatches. Their task is to coordinate the software and hardware components to act in accordance to what the user is asking for. Furthermore, OS do not have to be re-developed in order to create new apps, the latter can be built leveraging OS infrastructure.
Android is an open-source operating system for mobile devices and a corresponding open-source project led by Google.
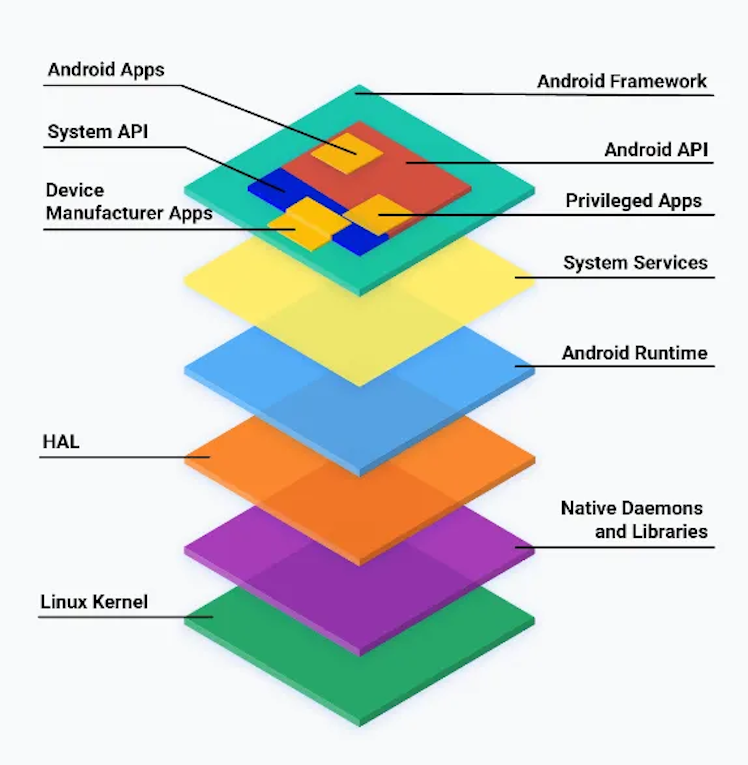
It is full of customizable source code that can be ported to nearly any device and public documentation. This means developers can utilize Android’s infrastructure, but changing some parts at will to create custom solutions that better suit their products.
Android Enterprise is a Google-led initiative to enable the use of Android devices and apps in the workplace. The program offers APIs and other tools for developers to integrate support for Android into their enterprise mobility management (EMM) solutions. Android Enterprise offers solutions for financial services, security, enrollment, management and employees.
This is one of Google’s historically monumental acquisitions. The company acquired Android in 2005 for 50 million dollars, but it was still in stealth mode. The first official version was released on September 2008. Google bought it under the following premise:
“Today’s announcement is more ambitious than any single ‘Google Phone’ that the press has been speculating about over the past few weeks. Our vision is that the powerful platform we’re unveiling will power thousands of different phone models.” Eric Shmidt, 2008
Again, Android is open-source and it’s free for anyone to install and use it. The business generates revenue through three different avenues. The first of them allows us to introduce another product Google has, Google Play Store.
Google Play Store
Google Play Store is the digital marketplace where all sort of apps can be published. The store was actually launched in March of 2012 with the intention of merging the previously known ‘Android Market’ and Google Services, like Google Music, Books.
As of May 2022, there were over 3.3million apps on Android App Stores. Its open-source approach allows developers to publish their apps in stores apart from Google’s, which explains the following image.
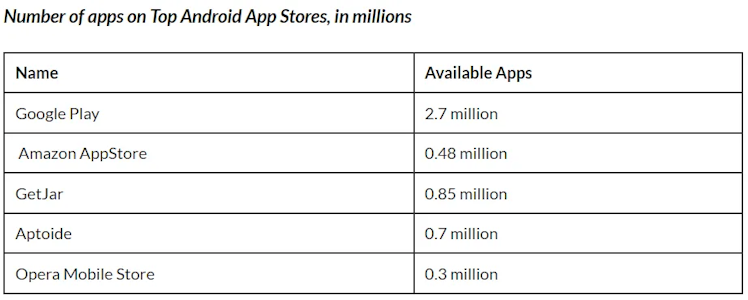
Being the intermediary between developers and users allows Google to cut its piece of every app purchased and every purchase made in-app, as it happens with every marketplace. It is estimated that the company’s take rate is 30% for the first-year subscription and 15% for all subsequent years.
To evaluate Google Play Store’s performance, I selected the number of applications downloaded each year and how many apps were there available as well. Both of them should be helpful to observe how has supply and demand trended over time.
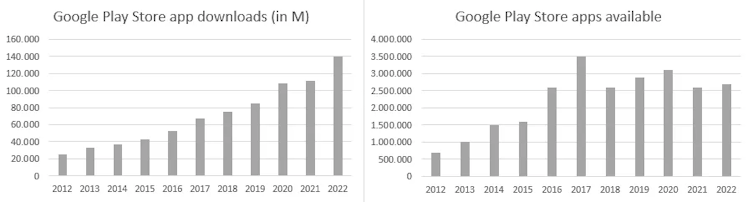
Since the official release of Google Play Store in 2012, the ecosystem went through a 5yr period of rapid growth, followed by a sequential slowdown.
- App downloads grew at an 18.8% CAGR, from 25bn downloads in 2012 to 140bn in 2022
- Apps available grew at a 14.5% CAGR, from 700 thousand to 2.7 million, though they are well below the peak in 2017 of 3.5 million
Android makes Google money from advertisements via two different sources.
- Firstly, developers that publish an app on the Play Store can opt for an advertising business model, from which Google would capture its share.
- Although Android in an open-source OS, this doesn’t mean that anyone can make changes that affect all Android devices. When a device manufacturer wants to use Android on their devices, they must agree to a set of terms and conditions set by Google, which includes some requirements for default apps. That’s why most Android devices come with Google Maps, Google Play, Chrome, etc, pre-installed.
This turns Android into an indirect advertising source of revenue. By having these set of apps as default, it ‘makes’ Android users utilize them, boosting Google apps usage and, with it, the advertisement revenue they generate.
In parallel to ads revenue, Google Play Pass was launched on September 2019. It is a subscription service offered by Google to Android users. By paying a monthly fee of $5 or $30 annually, Google offers customers hundreds of apps of all kinds, free of ads and in-app purchases. Included in Google Play Pass, there are games, productivity and creativity apps, educational, lifestyle and utility apps. The apps offered vary depending on the user’s location and the catalogue is constantly monitored and renovated. As of today (1Q 2023), Google has not yet disclosed how many subscribers Google Play Pass has.
After analyzing all integrated features, products and services to Android OS and how does it earn money, a good proxy for its performance may be how has the ecosystem evolved. In line with Google Play, I’ll consider metrics such as users and developers. For the following and almost all charts, keep in mind one thing. Google doesn’t really disclose anything on a yearly basis, so most numbers are rough estimates. Regarding this particular one, it begins in 2011 because numbers were very tiny before, with 9M users and one thousand developers.
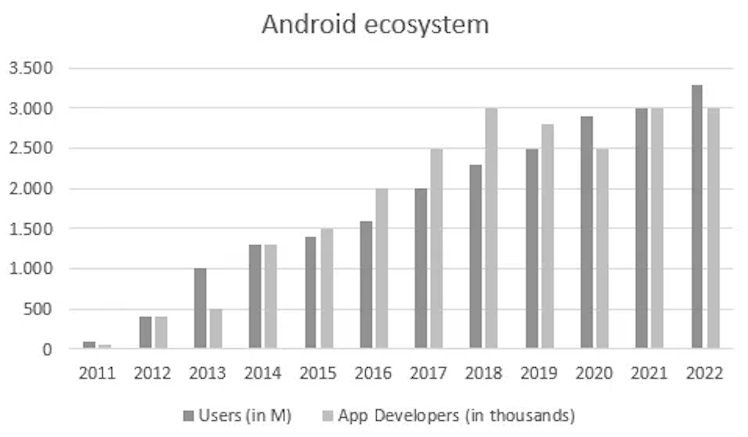
Since 2011, users have increased at a 38% CAGR, from 90M to around 3.3bn. On the other hand, Android app developers have increased at a 45% CAGR, going from 50 thousand in 2011 to around 3 million in 2022.
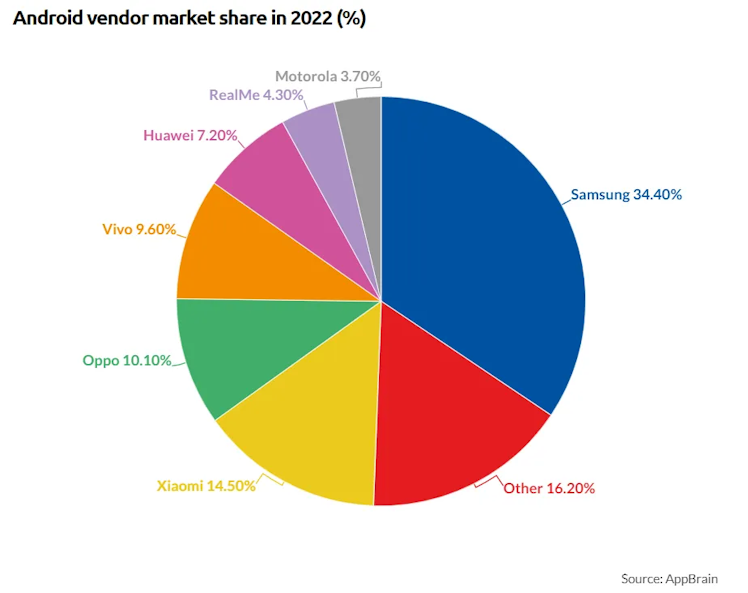
The last chart I’ll be sharing in this Android’s section is each vendor’s market share. Although this is not of extreme relevance, through these statistics, some insights could be potentially inferable. For instance, how much, relatively, does Google pay each vendor for the search engine to be default and how much dependence does Android have in each vendor.
Already have an account?